Climate change and environmental sustainability are both immense challenges that humanity faces. Nevertheless, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and the Internet of Things all have the power to support greener, eco-friendlier economic growth. Deploying sensors, smart devices, renewable energy systems, and optimized infrastructure across sectors means societies can monitor environmental footprints, conserve resources, and build sustainable futures. Global sustainability will depend heavily on technological advancements and innovation.
Monitoring Usage Through Connected Sensors

According to the experts at Blues IoT, a foundation for progress is real-time data monitoring to identify usage patterns and problematic areas using Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. For example, utility providers are deploying smart power and water meters that transmit household consumption data via wireless networks. When the data from all homes is aggregated, it reveals distinct periods of high energy demand. For the purpose of efficient resource management, companies now employ sensors to monitor both the inflow of resources into their facilities as well as the outflow of waste materials. With better tracking comes accountability – while also guiding interventions using evidence.
Cities likewise embed IoT devices to measure air quality, traffic flows, building efficiency, and more to inform policymaking. These integrated measurement and analysis systems, called “smart cities”, optimize energy, mobility, economic activity and daily functioning. They allow leaders to test sustainability initiatives and quantify improvements over time that are supported by data. The ability to intelligently monitor progress is essential not only for gaining insight into our current state but also for comprehending how future innovations will further the advancement of green initiatives.
Optimizing Systems Processes Intelligently

Smart systems go beyond basic sensing; they employ sophisticated analytics to automatically make fine-tuned adjustments, leading to a significant decrease in their environmental footprint. Smart power grids balance electricity distribution using AI, for instance, minimizing transmission losses and enabling smoother integration of renewables. Intelligent transport networks model congestion patterns to control traffic lights and adaptively coordinate autonomous electric vehicles someday. Through the use of machine learning, smart buildings are now able to optimize their heating and cooling systems, taking into account factors such as occupancy, weather forecasts, and the effectiveness of building insulation.
Combining connected sensors with automated analytics and control systems means resource usage across infrastructure, transportation, buildings, manufacturing supply chains, and beyond can hyper-optimize dynamically around efficiency targets. The result is intelligent urban systems orchestrating citizens’ and businesses’ collective interactions to shrink environmental harms through fluid, data-based adaptations targeting sustainability.
Deploying Sustainable Energy Solutions

Technology also speeds up sustainable energy production through renewable sources like solar and wind. Using big data analysis, companies determine ideal locations for solar plants factoring in weather patterns, transmission infrastructure, and changing efficiencies of photovoltaic panel technologies. Drones provide aerial inspection and maintenance of remote wind farms, and networked battery systems stabilized by algorithms enable larger grid integration of intermittent clean energy outputs.
Looking ahead, innovations like bacteria-powered fuel cells, bladeless wind turbines, kinetic pavement blocks, and solar windows offer radical sustainability advances. With so many technology-enabled options maturing simultaneously now, communities can transition toward renewable, reliable energy networks meeting present and future needs.
The Responsibility of Tech Leaders
Nonetheless, achieving widespread adoption of eco-friendly economies also demands that technology leaders drive cultural change. Companies must set science-based emissions targets, stress-test operations under climate scenarios, and transparently report progress. AI researchers have a duty to ensure algorithms make socially/environmentally beneficial recommendations too.
Every firm needs sustainable technology policies that assess environmental impacts across hardware life cycles. This includes minimizing toxic rare materials usage in devices, maximizing recyclable components, and supporting upgrading and repairing over disposal. With technology now permeating modern life, the industry bears great responsibility to build sustainability thinking intrinsically into products.
Collective Action for Systemic Progress
Governments also have pivotal roles in transitioning societies through regulations, incentives for green innovators, public R&D funding, and leading by example. International scientific collaborations generates consensus guidance, while cooperation between regulators avoids contradictory policies and, crucially, individuals must contribute through conservation habits, energy-aware purchases, political activism, and teaching future generations to be sustainability-minded.
With commitment across public, private and civil spheres, smart technologies can profoundly enable the systemic changes needed for a sustainable planet. Though the road ahead remains challenging, emerging tools provide hope that humanity backed by innovation can create more ecologically harmonious tomorrows.
Renewable Energy Technology Advancements
Advances in renewable energy technologies are ongoing. Scientists continue improving solar cell materials and designs to increase efficiencies and lower costs. Meanwhile, new manufacturing techniques using graphene promise lighter, highly conductive wires to enhance long-distance power transmission across national grid networks and leveraging big data analysis and machine learning, companies are developing sophisticated predictive models to better forecast intermittent solar and wind outputs hours or days ahead to smooth grid operations.
Circular Bioeconomy And Waste-To-Energy Innovations
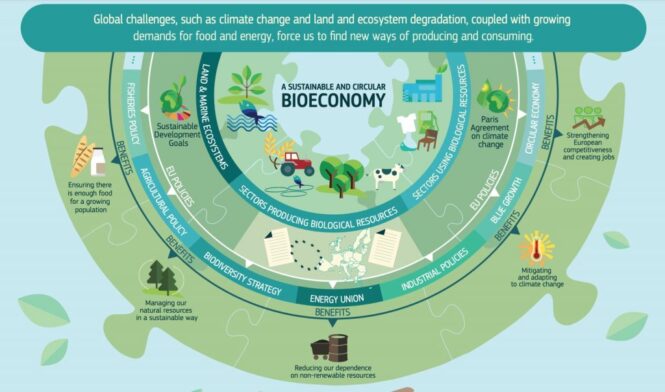
Sustainability-enhancing innovations also come through tapping the circular bioeconomy and reimagining waste streams as recoverable resources. For example, anaerobic digesters produce biogas fuel from food waste that communities can use to power municipal vehicle fleets, offsetting fossil fuel usage. And applying principles of industrial symbiosis, byproducts from one industrial process become inputs for another, closing resource loops locally. Smart waste-to-energy systems and bio-sourced materials will grow more common as technologies mature and supportive policies incentivize adoption.
With advancements across smart cities, intelligent infrastructure, renewable energies, biological processes, and prescriptive analytics, achieving sustainable development appears more viable than ever, if societies can recognize and harness technology’s potential fully. Converging rapid progress across domains, principally guided by environmental stewardship means tomorrow’s green economic system waits within reach.
Conclusion
Climate change threatens societies worldwide through rising seas, extreme weather, ecosystem damage and more. Sustainability-focused economic development supported by technologies offers solutions balancing environmental priorities and growth. Intelligent monitoring provides insight, while automated green systems optimization and clean energy transitions promise a more resilient path ahead. Deploying sensors, data analytics, algorithms, renewables and future tech innovations holistically will allow nations to work toward shared global sustainability, one step at a time.
 Imagup General Magazine 2024
Imagup General Magazine 2024



