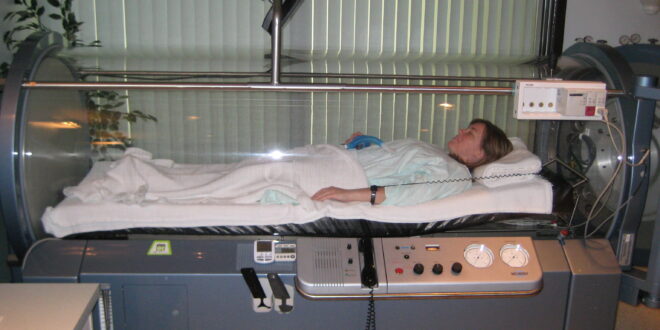
A medical procedure called hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has drawn interest due to its potential to cure a number of ailments. In this therapy, one must breathe pure oxygen in a chamber or room under pressure.
The body can absorb more oxygen at elevated pressure than it would normally be able to, which is believed to aid in the healing process and fend against infection.
This article explores the efficacy of HBOT and offers data on its success rates in various contexts.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
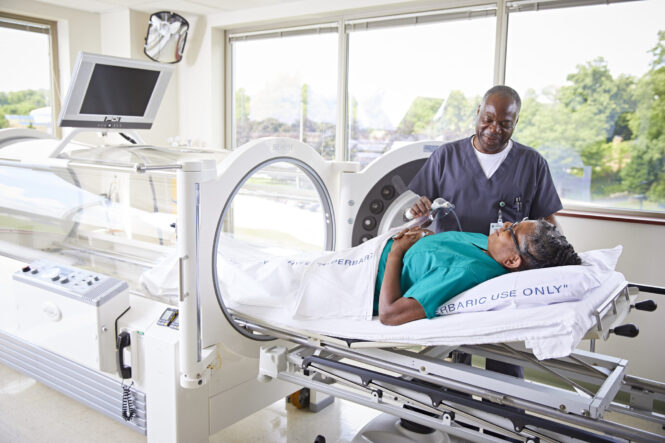
A non-invasive therapeutic technique called hyperbaric oxygen therapy has demonstrated promise in promoting the recovery of a number of illnesses. This section describes the basic ideas and gives an introduction to it.
HBOT works on the principle of increasing atmospheric pressure to enhance the amount of oxygen your blood can carry. This process aims to improve the oxygen supply to damaged tissues, potentially accelerating healing.
Studies suggest that HBOT can be effective in treating conditions like diabetic foot ulcers, certain types of infections, and injuries where tissues are not getting enough oxygen.
A typical HBOT session, such as those you might experience in a Los Angeles hyperbaric chamber, involves entering a hyperbaric oxygen chamber, either alone or with other patients, and breathing pure oxygen at pressures higher than sea level.
Sessions can last from 60 to 90 minutes, depending on the condition being treated. The increased oxygen absorption aids in reducing inflammation, fighting bacteria, and promoting the growth of new blood vessels, which are crucial for the healing process.
Facilities in Los Angeles offer state-of-the-art chambers equipped with the latest technology to ensure patients receive the most effective treatment possible.
Efficacy in Wound Healing
One of the primary applications is in the treatment of wounds, particularly those that are difficult to heal due to diabetes or radiation therapy. This section examines its success rate in this area.
For patients with diabetic foot ulcers, it can be a game-changer. Research indicates that when used in conjunction with conventional treatments, HBOT significantly increases the likelihood of healing.
The therapy’s ability to enhance oxygen delivery to the ulcer site promotes tissue repair and fights infection, thereby reducing the need for amputation in severe cases.
Neurological Conditions
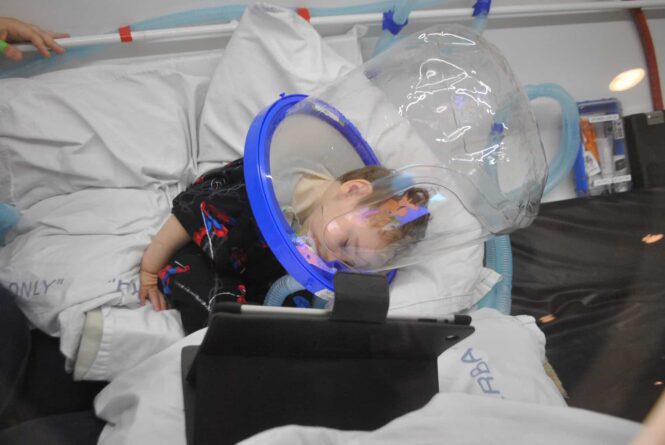
Potential benefits are not limited to wound healing; it also shows promise in treating certain neurological conditions. This segment explores its success in these areas.
The aftermath of a stroke can leave patients with significant challenges, including impaired motor skills and cognitive functions. HBOT has been studied as a treatment to improve outcomes after a stroke.
Evidence suggests that the increased oxygen levels can help revitalize brain tissue that has been damaged but is not yet dead, potentially improving function in stroke survivors.
Considerations and Contraindications
While HBOT shows promise, it is not without its considerations and contraindications. This final section addresses important aspects prospective patients should be aware of.
Generally, HBOT is considered safe when administered correctly. However, like any medical treatment, it can have side effects. The most common include ear pain, temporary vision changes, and, in rare cases, oxygen toxicity.
It is vital for patients to discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Advancements in HBOT Technology
Recent advancements in hyperbaric oxygen therapy technology have significantly improved the accessibility and effectiveness of treatments. Modern HBOT chambers are more comfortable and user-friendly, allowing for a better patient experience.
Innovations such as portable hyperbaric chambers have made it possible for patients to undergo treatment at home, under the supervision of medical professionals.
These technological improvements have not only expanded the reach but have also enhanced its potential benefits by making treatments more consistent and tailored to individual needs.
The Role of HBOT in Infectious Diseases
Particularly for infections involving anaerobic bacteria, which flourish in low-oxygen settings, HBOT has demonstrated potential as an adjuvant treatment. HBOT can stop these germs from growing and strengthen the body’s defenses against them by saturating the air with oxygen.
Positive results from studies on its application in the treatment of diseases like necrotizing fasciitis (a flesh-eating illness) and osteomyelitis (a bone infection) demonstrate the effectiveness of HBOT in battling infections that are resistant to conventional therapies.
HBOT and Cardiovascular Health
Emerging research suggests that hyperbaric oxygen therapy may have benefits for cardiovascular health. The enhanced oxygenation of the blood can improve circulation, reduce inflammation, and encourage the formation of new blood vessels, a process known as angiogenesis.
These effects could potentially aid in the recovery from heart attacks and improve outcomes for individuals with peripheral arterial disease. While more research is needed to fully understand impact on cardiovascular health, early findings are promising.
Psychological and Neurological Benefits of HBOT
Beyond its physical health benefits, HBOT may offer advantages for psychological and neurological well-being. Studies have explored its use in treating depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), with some patients reporting improvements in symptoms.
The increased oxygen levels are thought to promote neural health and may help to repair brain function affected by these conditions. This area of research is still in its early stages, but it opens up new possibilities for using HBOT in mental health treatment.
Future Directions for HBOT Research
The potential applications for hyperbaric oxygen therapy continue to expand as research delves into new areas. Future studies are likely to explore its use in aging and neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Researchers are also investigating the mechanisms behind HBOT’s effects on the body at the molecular level, which could lead to targeted therapies for a range of conditions. As the body of evidence grows, HBOT may become an increasingly integral part of holistic medical care, offering new hope for patients across a spectrum of diseases.
Conclusion

In conclusion, Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy holds significant potential in treating a variety of conditions, from chronic wounds to neurological impairments.
Its success rates vary depending on the condition being treated, but the evidence supporting its efficacy is growing. As with any treatment, individuals should consult with healthcare professionals to understand the risks, benefits, and whether HBOT is right for them.
Through careful consideration and proper application, HBOT can be a valuable tool in the medical arsenal, offering hope and healing to many.
 Imagup General Magazine 2024
Imagup General Magazine 2024